This next age of medicine will revolve
around stem cells.
Talk to an expert:
+48 605 113 067
Our regenerative capacity diminishes with age. Very few tissues and organs can spontaneously regenerate following disease or trauma.
Stem cells are the building blocks of the human body. They are the foundation cells in our blood, bones, skin and organs. Throughout our lives, we rely on stem cells to replace injured tissues and cells that are lost every day. Unfortunately they deplete with age, and therefore our ability for the body to self-repair is hampered as not enough stem cells reach the affected area to repair the damage in the body.
Stem cells therapy is an innovative and safe treatment using cells naturally present in our body’s and the body’s natural healing process to heal certain degenerative conditions, reduce inflammation, and accelerate and enhance injury recovery by regenerating healthy tissue.
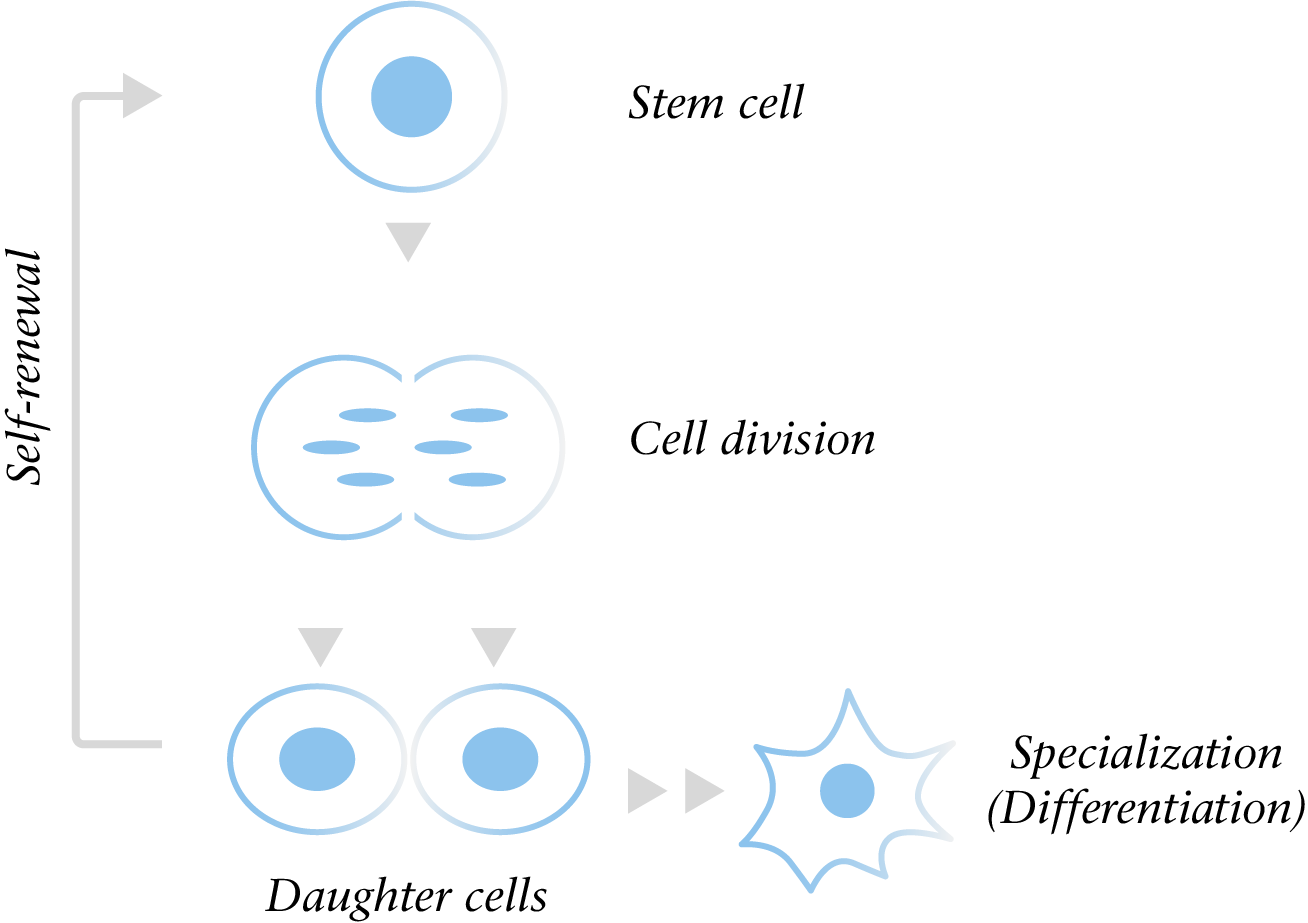
Stem cells possess two key properties:
DIVIDING
The ability to self-renew; dividing and making copies of themselves.
DIFFERENTIATING
The ability to differentiate; to develop into specialized cell types in the body.
At Life Institute we focus on the application of Adult Stem Cells and not Embryonic Stem Cells.
Embryonic stem cells come from embryos that are three to five days old, they only exist at the earliest stages of development. There are ethical concerns with embryonic stem cells as they are primarily harvested from destroyed human embryos left over from in-vitro fertilization.
Although adult stem cells are less powerful than embryonic cells, they are easier to use as we all have our own supply of cells throughout our bodies. They are abundant, found in many tissues and organs; adipose (fat) tissue, bone marrow, blood vessels, skeletal muscle, skin, teeth, heart, gut, liver and brain to name a few.
MESENCHYMAL STEM CELLS (MSCs)
Multipotent mesenchymal stem cells are adult stem cells which can be found throughout the body including adipose (fat) tissue, umbilical cord (Wharton’s Jelly), bone marrow, amniotic fluid and other tissues and organs.
They are appropriate for stem cell therapy as they self-renew differentiate into multiple cell types such as:
Adipocytes - cells that specialize in storing energy as fat,
Chondrocytes - cells found in healthy cartilage,
Osteoblasts - cells that form new bone,
Tenocytes - cells involved in tendon healing, responsible for the maintenance of extracellular matrix and collagen.
Healthy cells are used to replace diseased cells. MSCs can be guided into becoming specific cells, though the specific cell they become is related to the organ/tissue to which they are located. They are used to regenerate and repair diseased or damaged tissues, in the process regulating the inflammatory, fibrotic and tissue remodeling responses. As MSCs are biologically compatible they do not risk rejection.

Multipotent
Having the capacity to self-renew by dividing and developing into multiple specialized cell types.
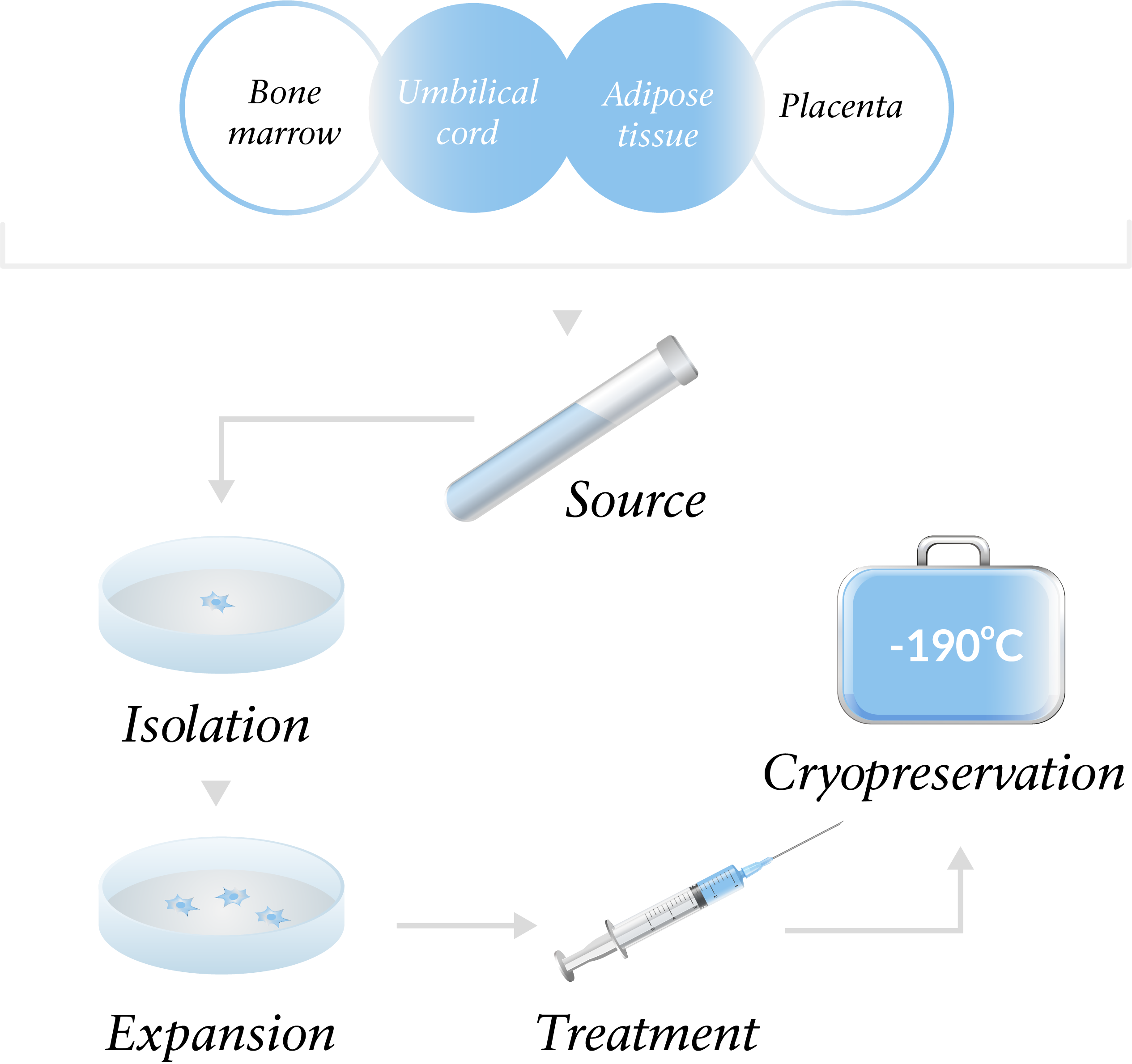
At Life Institute we focus on two sources of MSCs:
Adipose Stem Cells, autogenic (own) cells (adMSC)
A key advantage of mesenchymal stem cells from the patient’s own fat tissue (versus for example bone marrow) is that they can be easily and repeatedly harvested, isolated and expanded.
They display stable growth properties and can be extracted using minimally invasive techniques with very low morbidity (cell death rate).
As they are taken from your own body, there is extremely low risk of disease transmission or allergic reactions. There is also no chance of the cells causing cancer, as adipose cells are adult cells.


Wharton’s Jelly, allogenic (donor) cells (WJ-MSC)
The umbilical cord has one vein and two arteries. Surrounding and protecting these vital blood vessels is a sticky, jelly-like substance called Wharton’s Jelly, which itself is covered by a membrane called the amnion.
WJ-MSC’s have immunomodulatory properties involving both innate and adaptive immune responses. They have high proliferation (able to make copies of themselves) and differentiation capabilities, meaning they can be induced to differentiate into mature cell types.
They can be easily accessed and collected, which results in no legal or ethical issues.
They are a potent source of adult cells, which for example, can be used in older patients whose autogenic (own) cells, have limited therapeutic efficiency, primarily due to the result of the ageing process.
Immunomodulatory
Capable of modifying or regulating one or more immune functions.
How does stem cell therapy work?
Your joints and most body tissues contain stem cells which are responsible for the health in that location of the body. As we age, the stem cell population reduces, the degenerative process increases, and the body loses its capacity for self-healing.
By repopulating the area, stem cell therapy promotes the repair response of diseased, dysfunctional, injured or damaged tissue using healthy stem cells to restore the body’s ability for self-healing.
Unlike drugs which can be produced and tested in large batches, stem cell treatment is specific to each patient.
Our surgeons choose the appropriate MSCs (adMSC or WJ-MSC) for the best therapeutic effect, depending on the condition to be treated, your overall health and age.
Donor cells (WJ-MSC) are used in situations where;
- Laboratory qualification is not secured.
- Patients cells have low proliferation potential (ability to expand).
- Patients are over 55 years of age.
- When the therapy needs to start immediately (and there is no time
for the extraction, isolation and expansion phases).
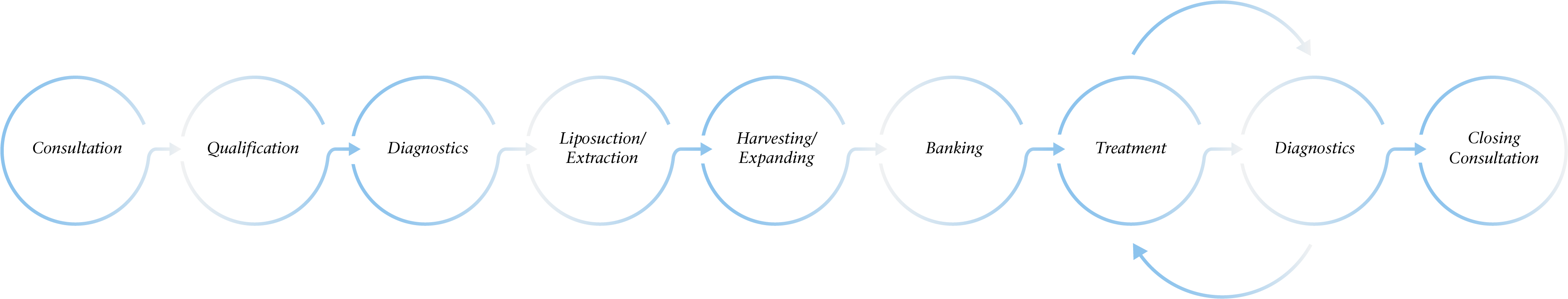
What does the process look like?
For WJ–MSC (donor) stem cell therapy, the treatments may start once you have qualified and completed the required diagnostics. The diagnostic and treatment steps will be repeated untill the end of your protocol.

For adMSC (own) stem cell therapy, the treatments will begin once the harvesting and expanding phase is complete, this can take up to 3 months. The diagnostic and treatment steps will be repeated untill the end of your protocol.